Prevention, Testing & Treatment
Sexually transmitted infections are passed from one person to another through any form of sexual activity. They can also be passed from one person to another through intimate physical contact though this is not very common. STDs don’t always cause symptoms or may only cause mild symptoms, so it is possible to have an infection and not know it.
Using condoms during sex or abstaining from sex with partners who are untested and whose sexual history you do not know are the only effective ways of preventing a sexually transmitted infection.
It is important to get tested if you are sexually active. If you are diagnosed with an STD, know that all can be treated with medicine and some can be cured entirely. Untreated STDs may result in pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women. Infection with the sexually transmitted Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) may lead to development of cervical cancer.
Chlamydia
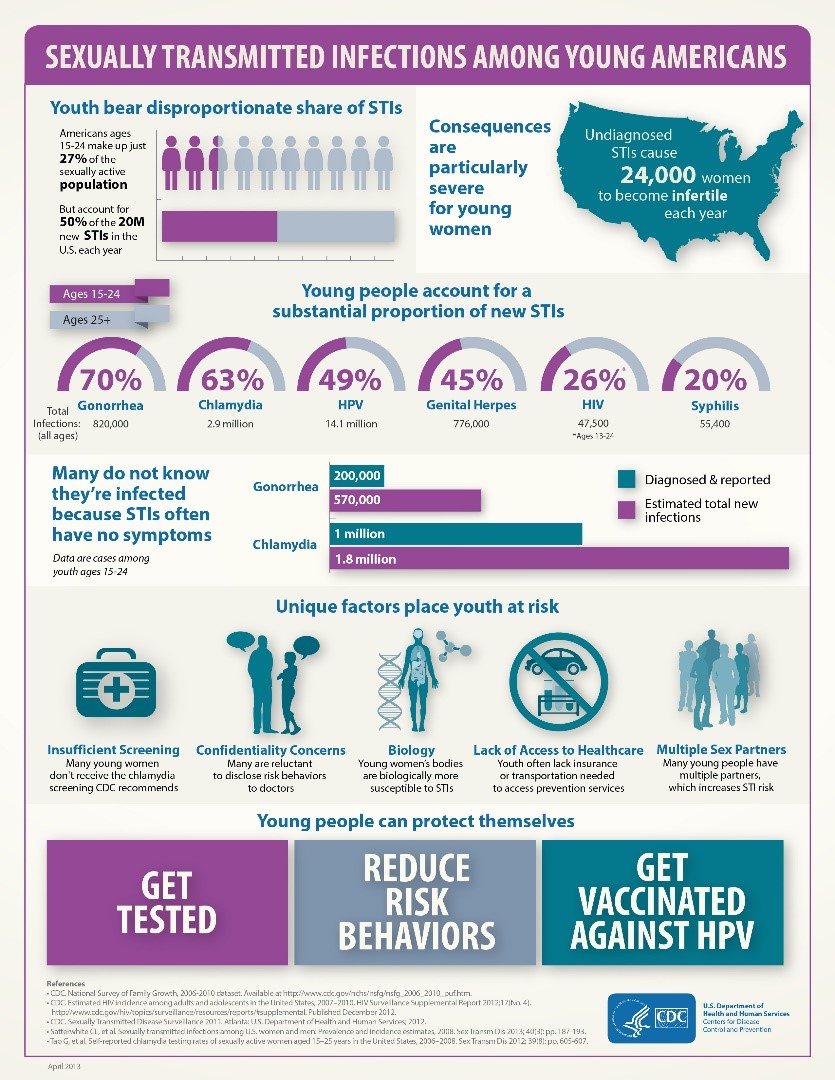
Chlamydia usually spreads through sexual contact, but may be passed from an infected mother to a baby during birth. Close to 3 million Americans get it every year, most commonly among 14-24-year-olds. Chlamydia can infect the penis, vagina, cervix, anus, urethra, eyes, and throat. Chlamydia can be cured but left untreated may lead to infertility in women.
Symptoms
Typically, chlamydia has no symptoms, however when symptoms do occur these can include:
-
Pain or burning while peeing
-
Pain during sex
-
Lower belly pain
-
Abnormal vaginal discharge (may be yellowish and have a strong smell)
-
Bleeding between periods
-
Pus or a watery/milky discharge from the penis
-
Swollen or tender testicles
-
Pain, discharge and/or bleeding around the anus
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is spread through contact with blood from an infected person. For some people, hepatitis C is a short-term illness. However, for more than half of people who become infected with the hepatitis C virus it becomes a long-term infection. Chronic hepatitis C can result in potentially life-threatening health problems.
The hepatitis C virus is usually spread when someone comes into contact with blood from an infected person. This can happen through:
-
Sex with an infected person.
-
Sharing drug-injection equipment.
-
Approximately 6% of infants born to infected mothers will get hepatitis C.
-
Healthcare exposures.
-
Unregulated tattoos or body piercings.
Sharing personal items such as glucose monitors, razors, nail clippers, toothbrushes, and other items that may have come into contact with infected blood.
Symptoms
Many people with hepatitis C do not have symptoms and do not know they are infected. If symptoms occur, they usually appear within 2 to 12 weeks, but can take up to 6 months to develop.
Symptoms can include:
-
Yellow skin or eyes
-
Not wanting to eat
-
Upset stomach, throwing up, and stomach pain
-
Fever
-
Dark urine or light-colored stool
-
Joint pain
-
Extreme tiredness
People with chronic hepatitis C can live for years without symptoms or feeling sick. When symptoms appear with chronic hepatitis C, they often are a sign of advanced liver disease.


Hours of Operation!
Monday – Friday
8:00am – 4:00pm
CONTACT
PHONE
(740)962-4572
Fax Number
(740)962-3271
ADDRESS
4275 N State Route 376,
McConnelsville, Ohio 43756
